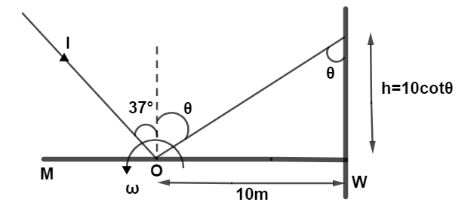
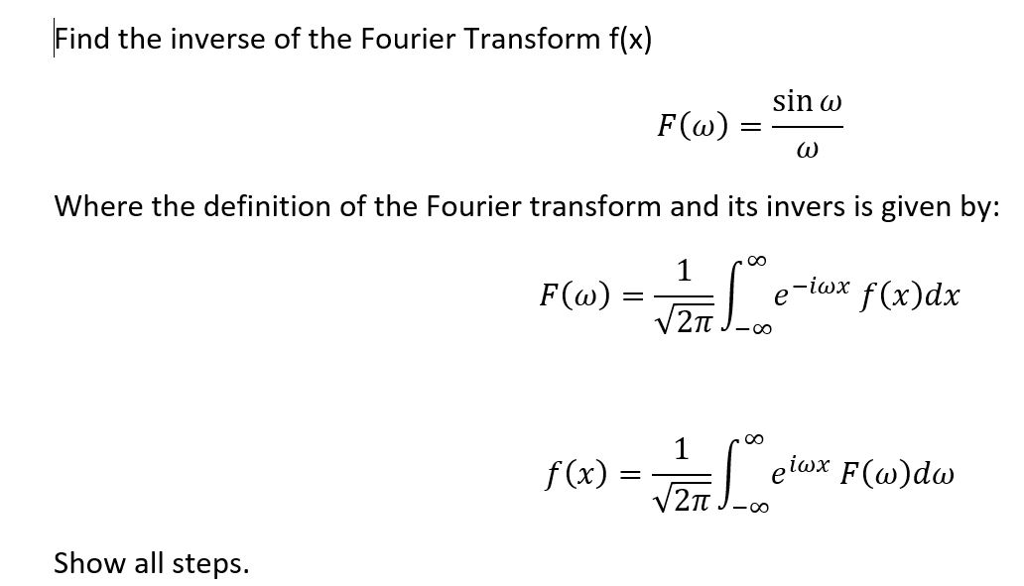
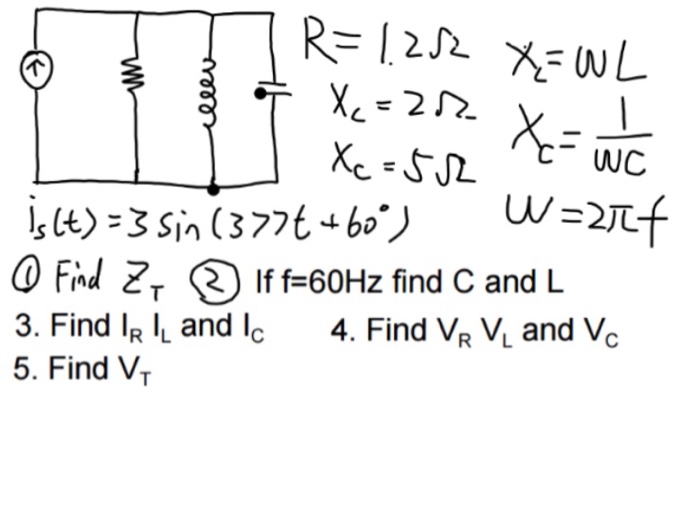
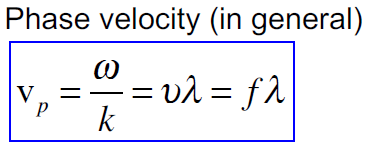Why do we sometimes calculate Fourier transform with omega (angular frequency) as a variable and some other time with f (frequency) as a variable? - Quora
Why do we sometimes calculate Fourier transform with omega (angular frequency) as a variable and some other time with f (frequency) as a variable? - Quora

Curve showing the evolution of the amplitude of $R$ as a function of... | Download Scientific Diagram
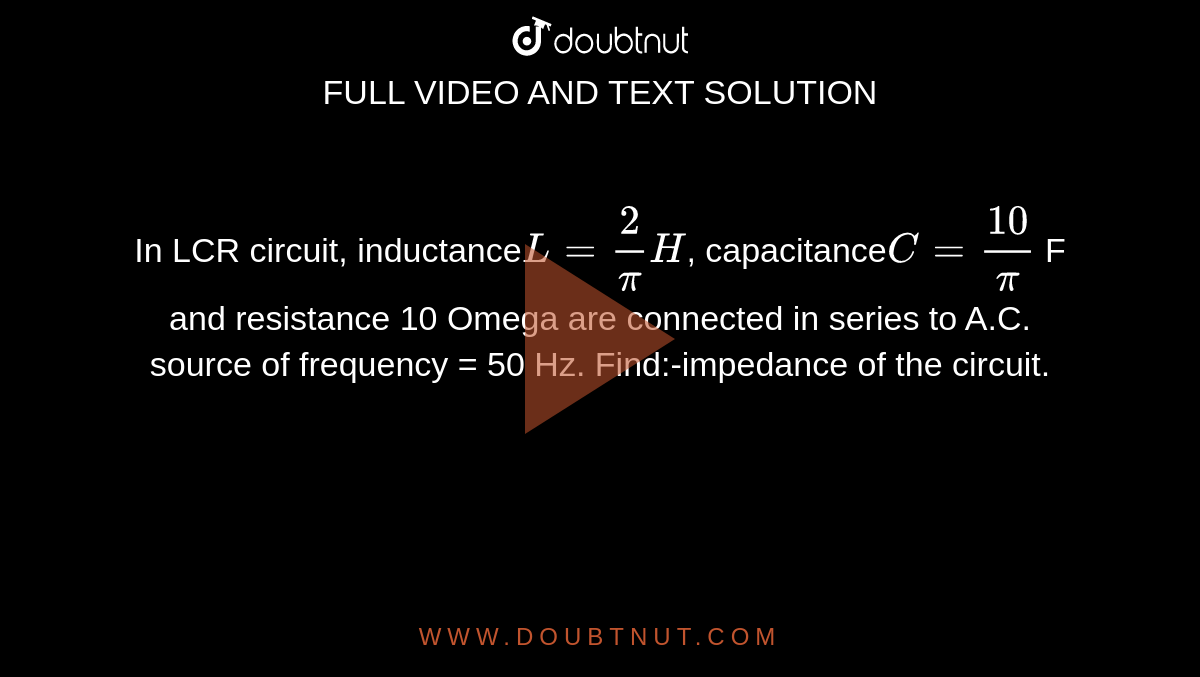
In LCR circuit, inductance L = 2/pi H, capacitance C = 10/pi F and resistance 10 Omega are connected in series to A.C. source of frequency = 50 Hz. Find:-impedance of the circuit.